Leadership and Lean Innovation
Boosting Employee Creativity in Singapore

The Singaporean Context: Challenges and Opportunities
Singapore, with its collectivist culture and high power distance, presents unique challenges for fostering innovative work behaviour (IWB). Employees often hesitate to “rock the boat” with new ideas, fearing the disruption of established routines.

Transformational Leadership: The Catalyst for Innovation
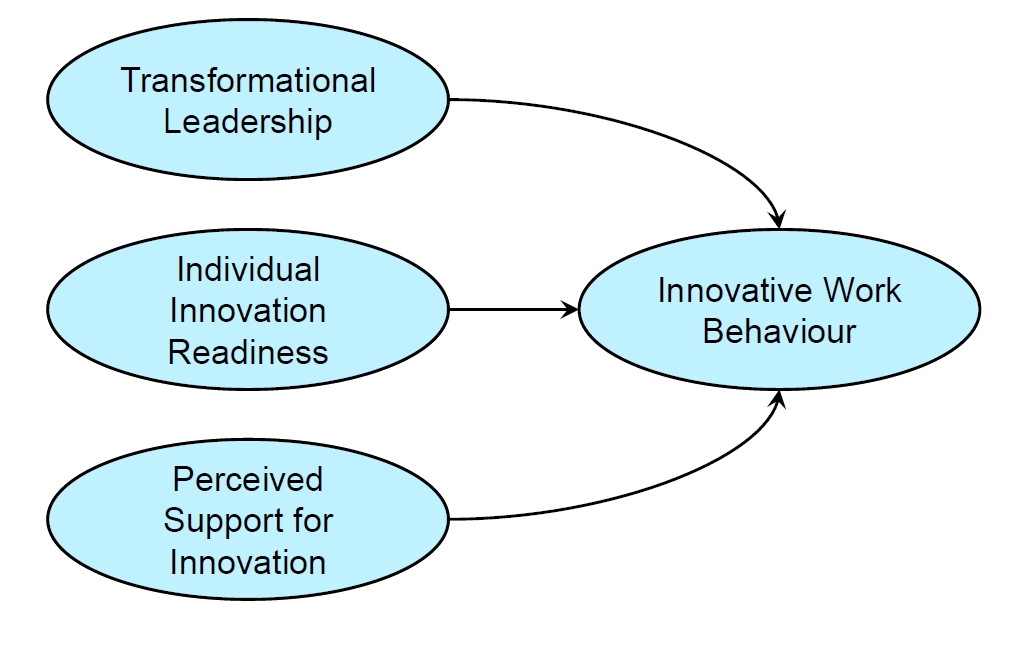
Perceived Support for Innovation: A Crucial Mediator

Lean Innovation Training: Building Creative Role Identity
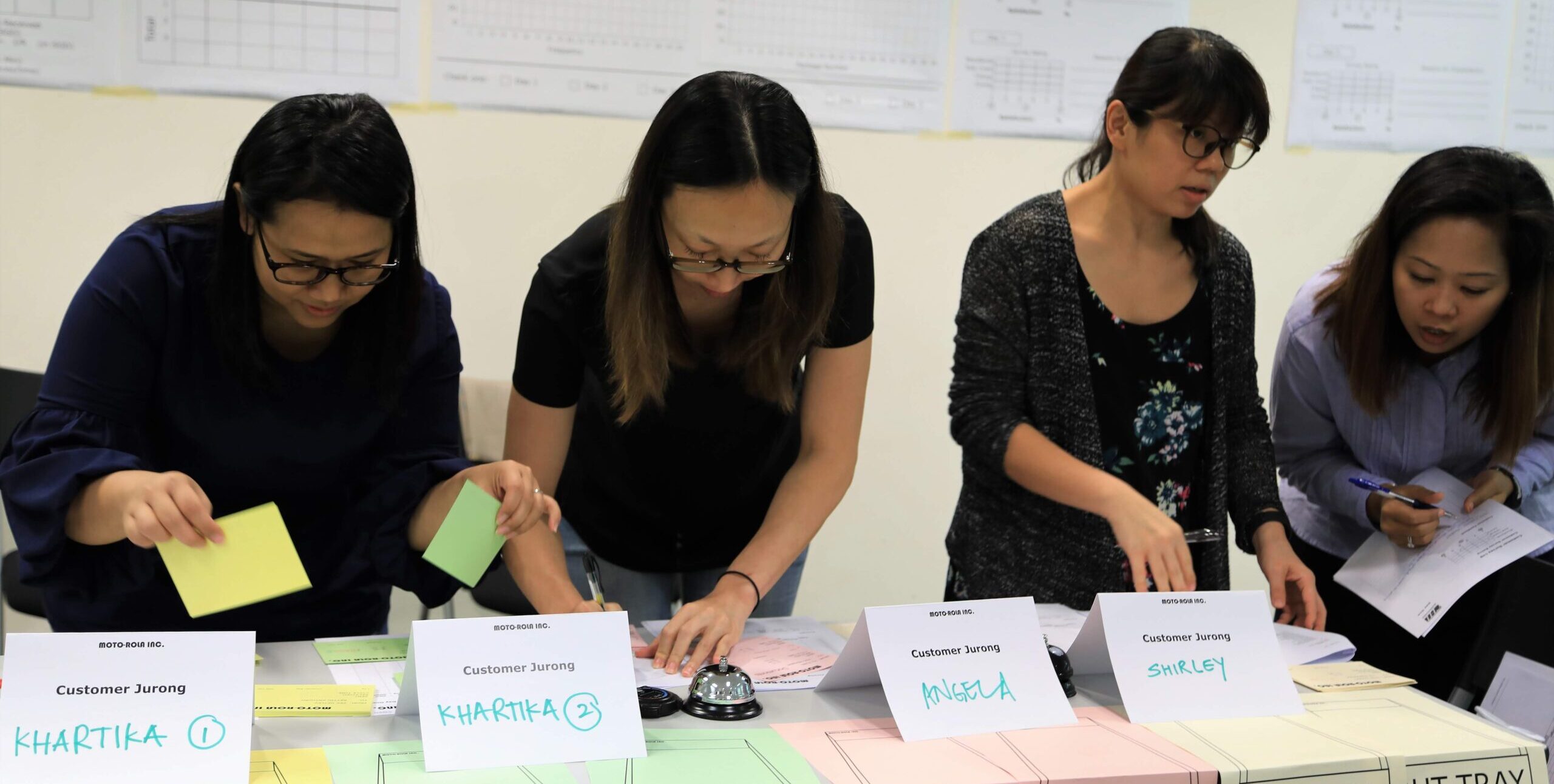
Lean Innovation Training (LIT), which combines Lean Six Sigma and Creative Problem-Solving (CPS) tools, has been shown to significantly boost employees’ creative role identities and innovative behaviours.

Empirical Studies: Insights from Singapore
Study 1: Transformational Leadership and IWB
The first study examined the relationship between transformational leadership and employee IWB using our Innovation Readiness Survey (IRS).
The findings confirmed that transformational leadership positively influences IWB, mediated by perceived support for innovation and innovation readiness (Tan, Van Dun, & Wilderom, 2021).
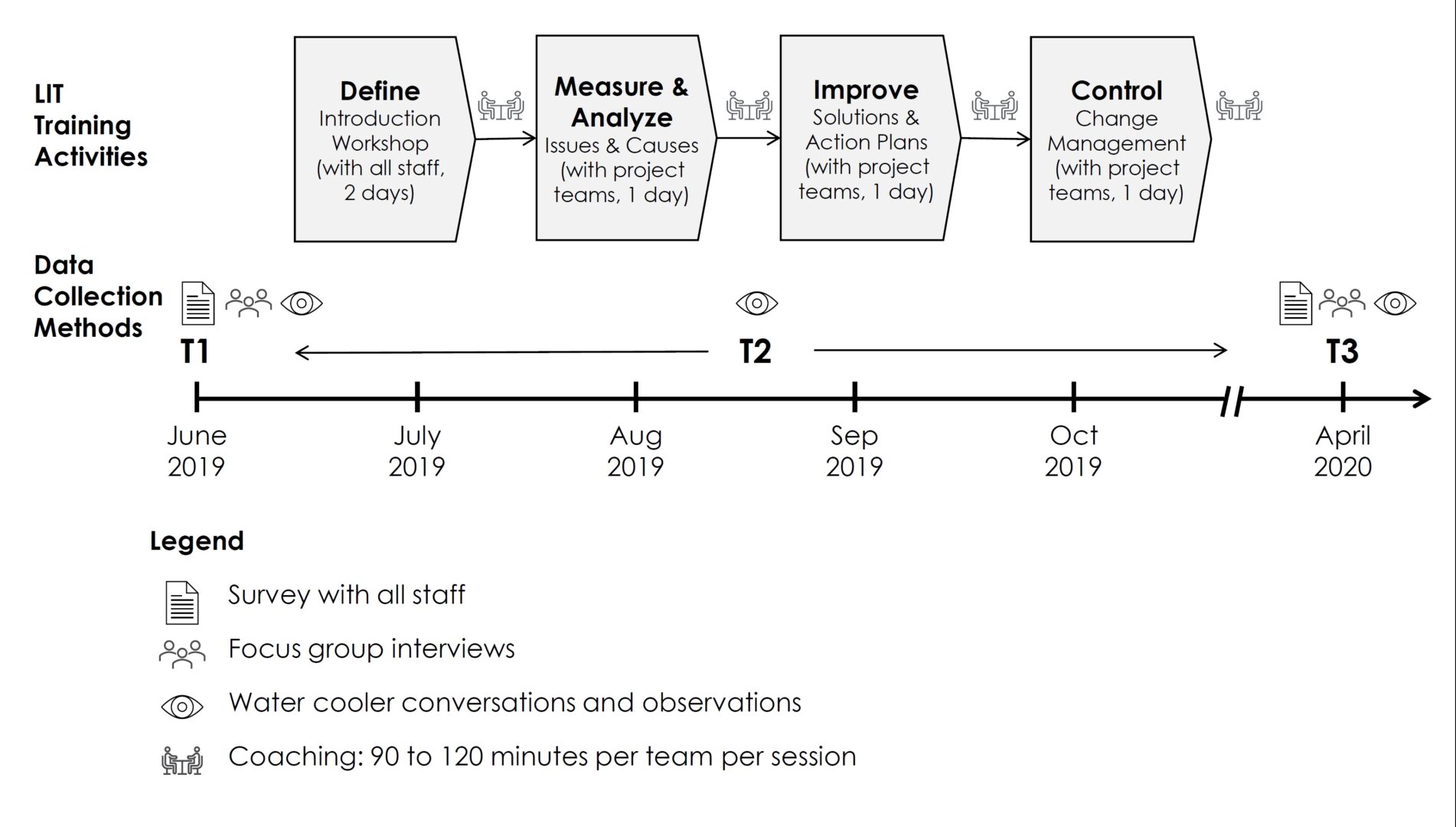
Study 2: The Impact of LIT on Innovation
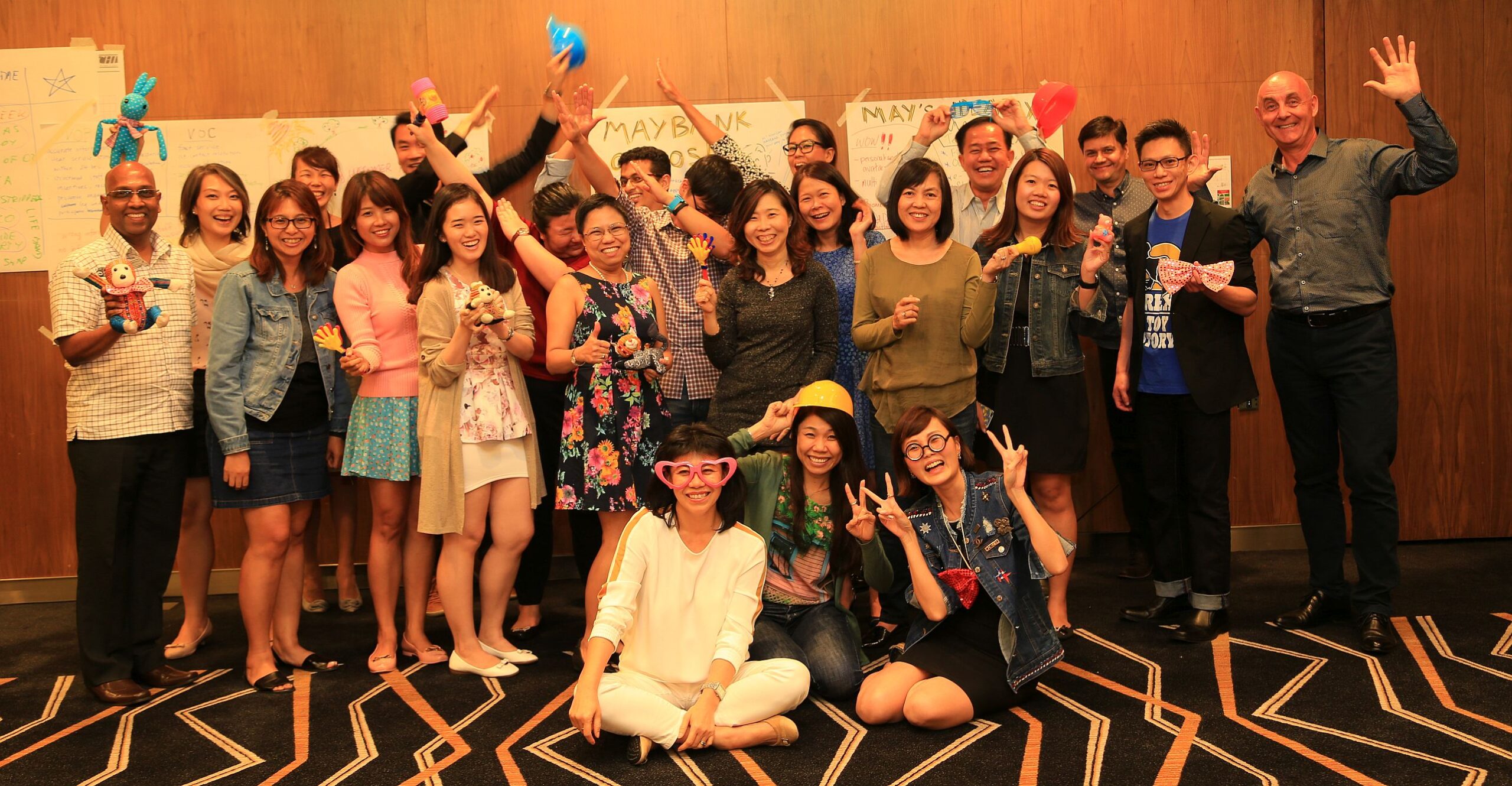
The second study focused on a public service organisation where Lean Innovation Training (LIT) was implemented. The results showed that LIT, coupled with transformational leadership, significantly enhanced employees’ creative role identity and IWB.
Employees felt more psychologically safe and supported, leading to higher levels of innovation (Tan, Van Dun, & Wilderom, 2023).
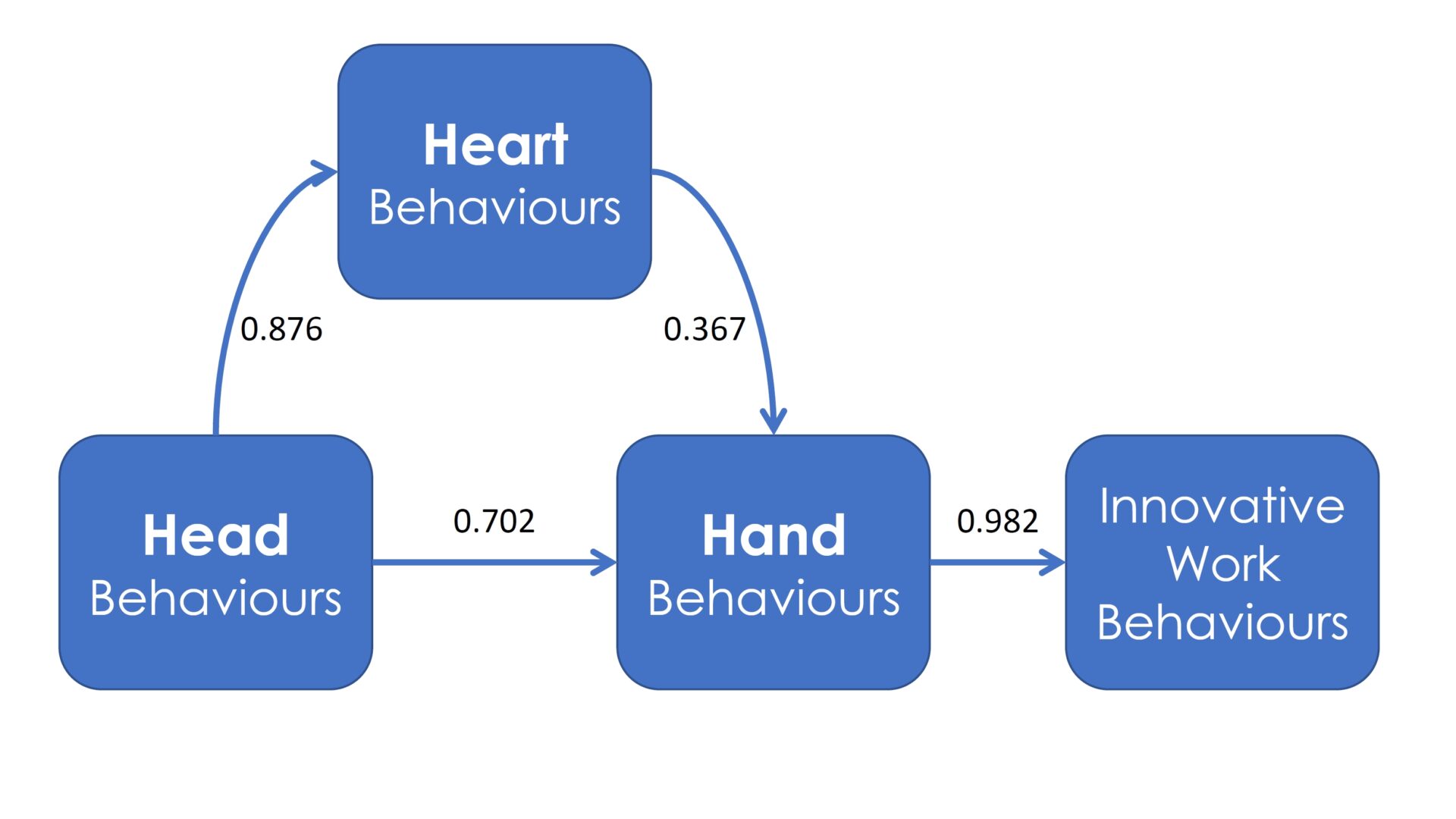
Study 3: Beyond Transformational Leadership
A new survey instrument, the Innovative Leader Survey (ILS), was developed and validated. This tool helps organisations assess and develop leadership behaviours that promote innovation (Tan, Van Dun & Wilderom, 2024) .
Practical Implications: Strategies for Success
- Implement Lean Innovation Training: Adopt LIT to build employees’ creative role identities. This training should integrate Lean Six Sigma and CPS tools, emphasizing hands-on, action-learning experiences.
- Create a Supportive Environment: Ensure that employees feel supported in their innovative efforts. Recognize and reward creativity, provide necessary resources, and foster an open, change-friendly culture.

- Use the Innovative Leader Survey: Utilise the ILS to assess current leadership behaviours and identify areas for improvement. Tailor leadership development programs to enhance behaviours that promote IWB.
Conclusion: Unleashing Innovation in Singapore

- All Posts
- Innovation









