The more important it is to identify drivers and hindrances for Innovation.
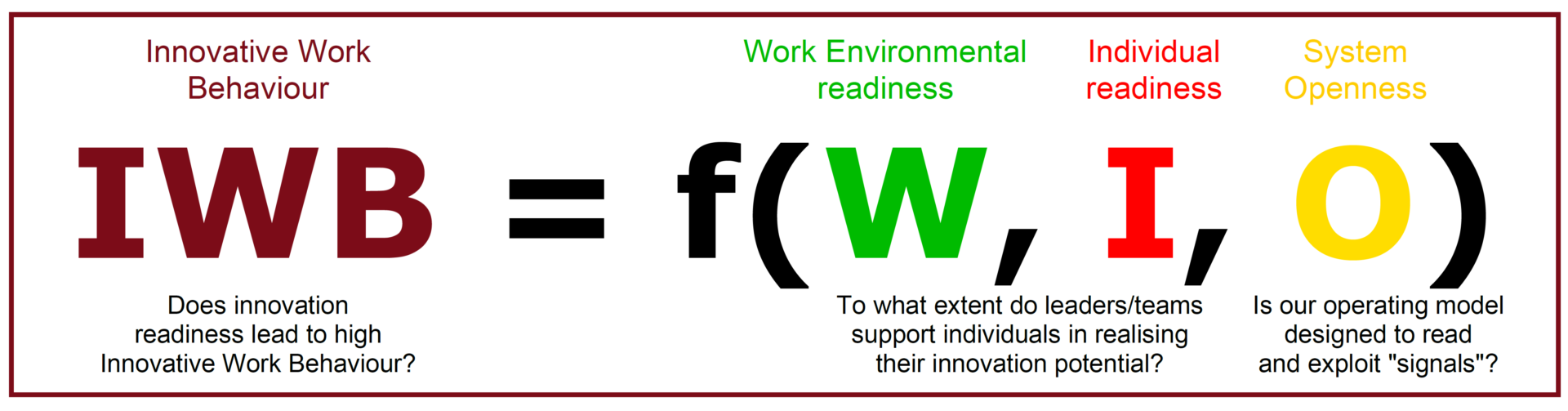
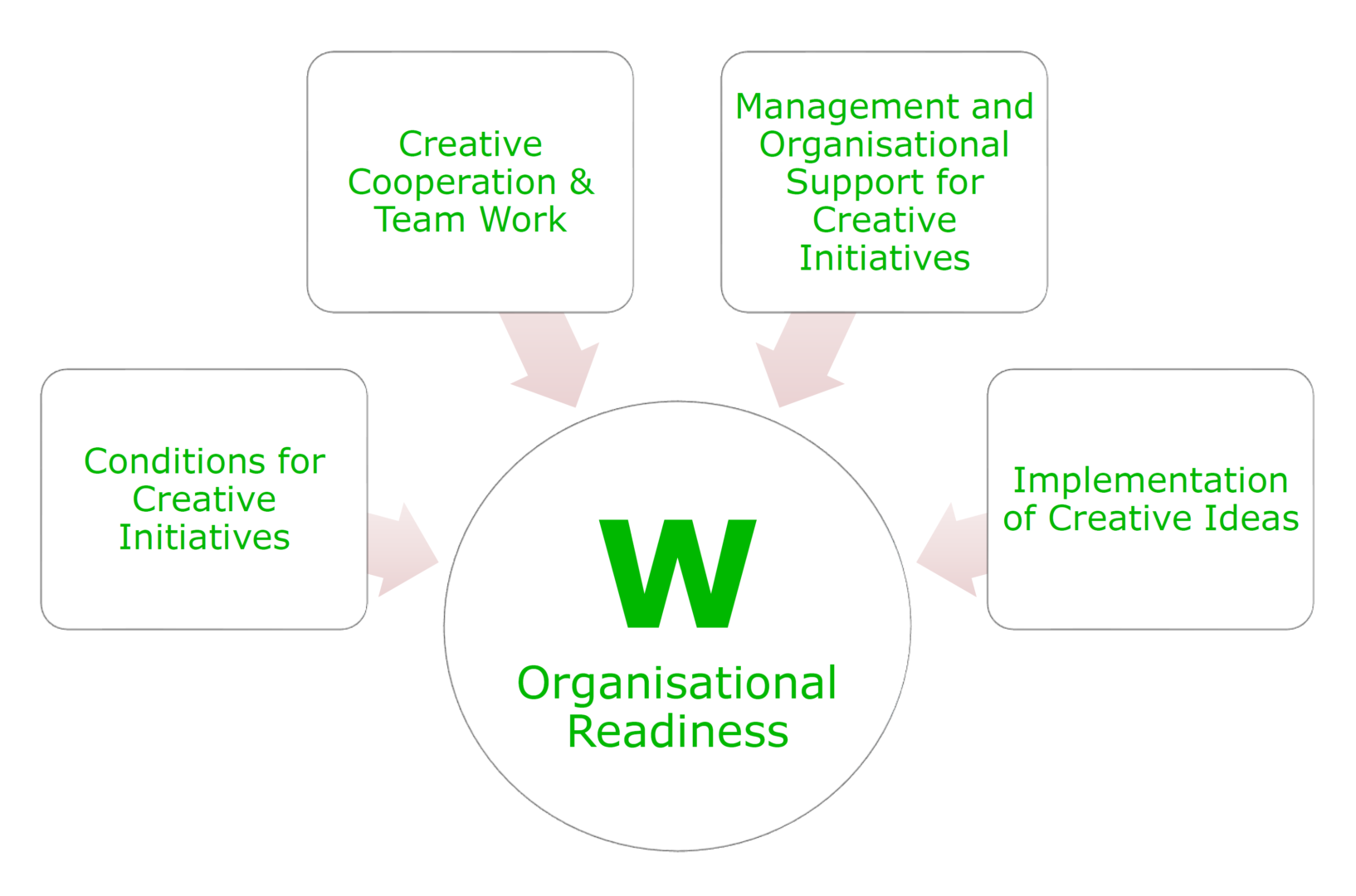
The Readiness to Innovate depends on basically three factors: Individual Creativity and Innovativeness, Support for Innovation and System Openness.
This article aims to explore the motivation for Individuals’ Innovative Work Behaviour (IWB) and hence their influence on organisation’s growth and success.
Can Our Staff Innovate?
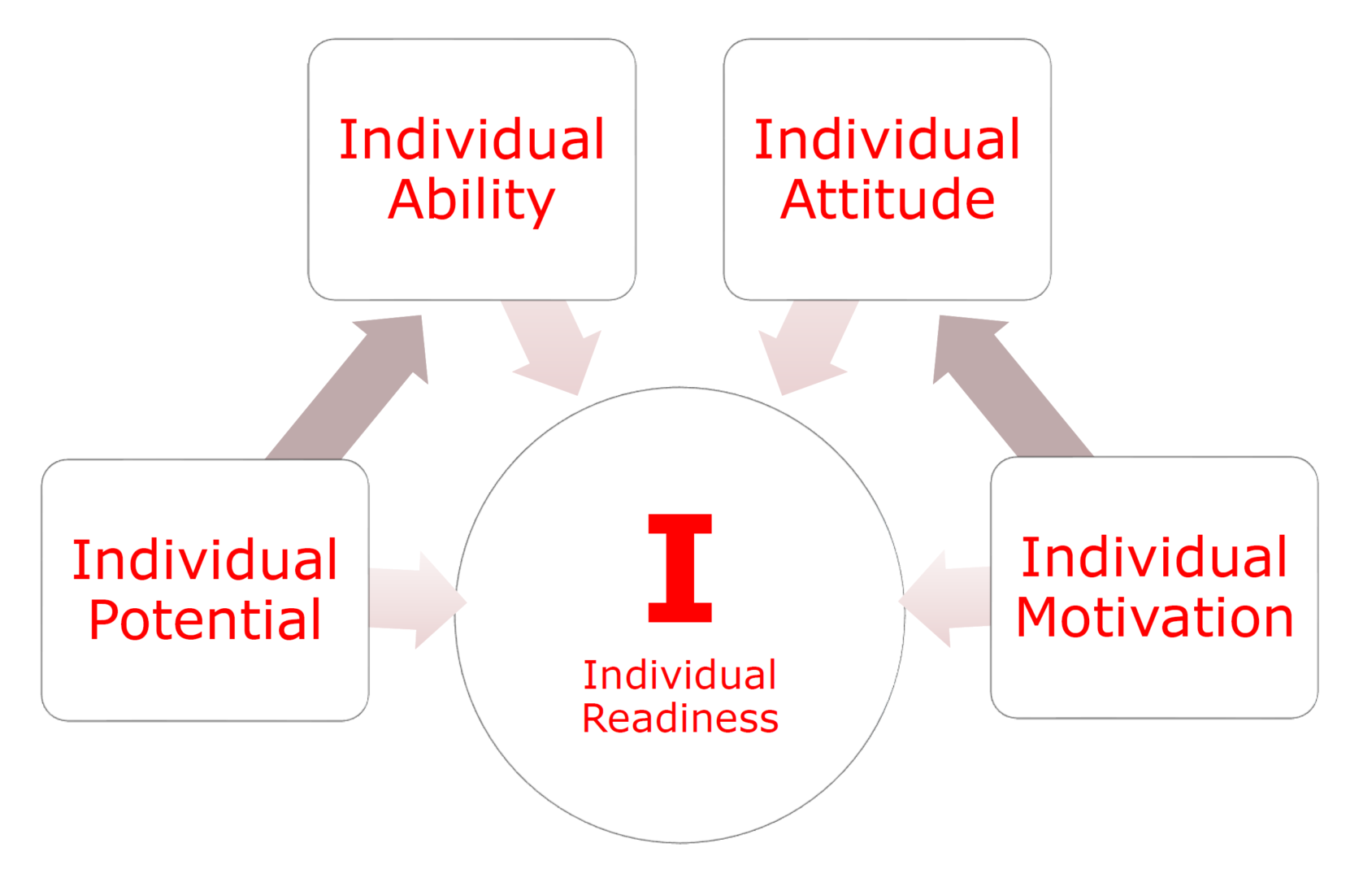
Each of us has the potential to innovate – we could generate great ideas, follow through in step-by-step actions and processes, and bring ideas to life. And, it is rather easy to use the potential and turn it into the ability to innovate. Can our staff innovate?
The question is not whether I can innovate (abilities) but rather whether I want to innovate (attitudes). As individuals, we have similar potential for being innovative but have different approaches to the process of innovation.
How Can Your Organisation Support Individual Innovativeness?
1. Encourage Risk-Tolerant Climate for Innovation
Provide employees with a Second Chance – Companies can foster a culture of risk-taking by giving employees a chance to recover from failures and providing them with encouragement to create new ventures. The former CEO of General Electric encourages risk-taking: “You can make mistakes! But, make sure you and the organisation learn from these mistakes to avoid them next time!”
Recognise and Accept Failure Among Senior Leaders – Failure-tolerant leaders help employees overcome their fear of failure and encourage risk-taking. Leaders shall communicate to employees that failure is acceptable and forgiven by admitting and talk about their own mistakes.
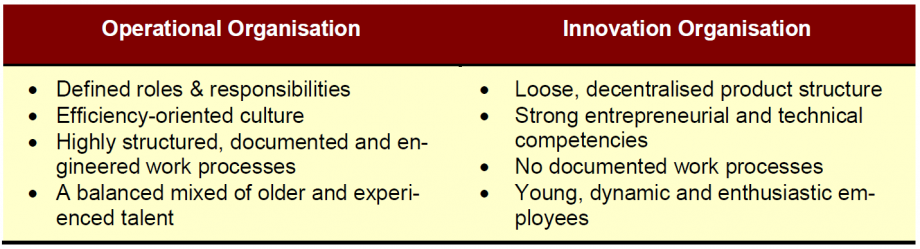
2. Modify Organisational Structure to Enable Innovation
3. Focus Recruitment Efforts on Innovation
These companies screen & select candidates who have creative intuition and also tailor interview questions to uncover the innovation tendencies of new individuals.
Tailor Interview Questions to Identify Innovative Tendencies – Some organisations use self-screening tools, traditional resume screening techniques and regional assessment centres to narrow the pool of candidates.
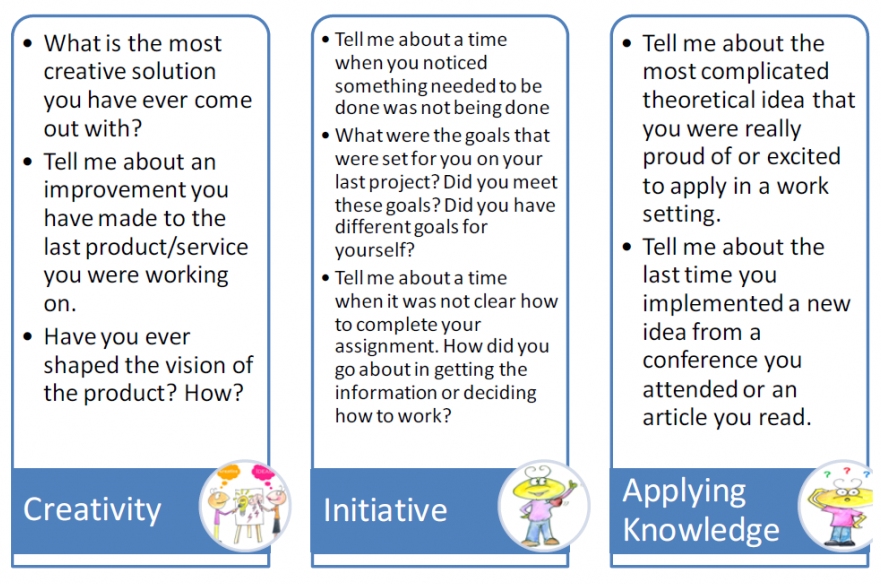
Measure for Individual’s Creativity – A rather creative individual can be identified through psychometric testing, including the Kirton Adaptation-Innovation Inventory (KAI). This test works under the assumption that individuals exhibit different problem solving styles leading to different forms of creativity.
4. Train to Cultivate Innovation Behaviours
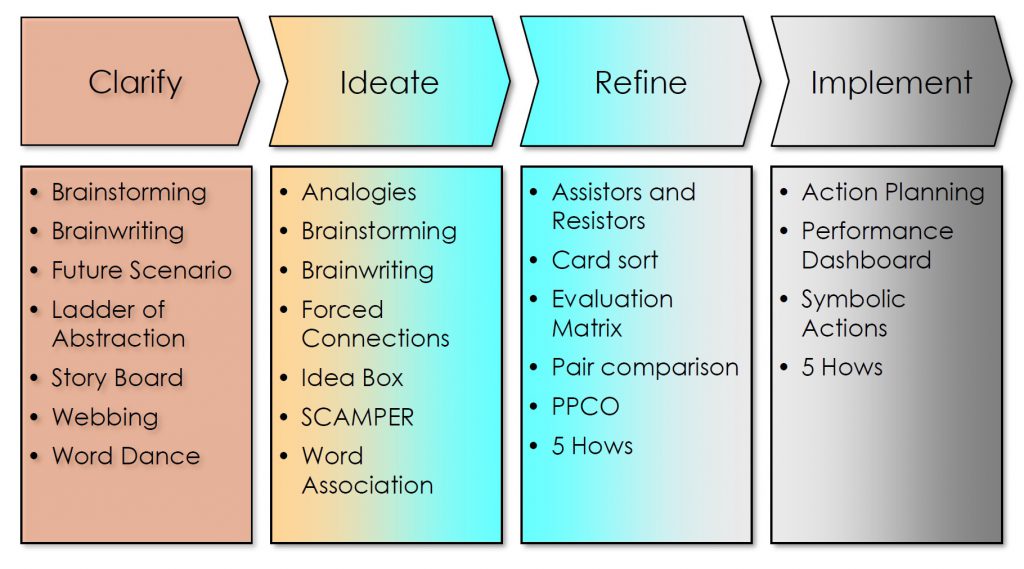
5. Establish Innovation Performance Expectations
The following behaviours were identified as supporting innovative work behaviour, amongst others:
- Apply Analytical thinking
- Be Knowledgeable
- Be Creative
- Take Initiative
- Be Open to New Ideas
- Show Customer Centricity
- Manage Risk

Some companies have also included references to creativity and innovation to their leadership competency framework to hold leaders accountable for developing creative enterprise.
6. Motivate Innovation via Reward & Recognition
Conclusion
Leaders play a vital role in providing adequate innovation climate so as to encourage individuals to bring the best innovativeness to the organisations.
Solely investing in training employees on creativity tools & techniques will not lead to a higher degree on innovation. Yet, it might be necessary.
- All Posts
- Innovation








